In the ever-evolving landscape of customer data management and engagement, distinguishing between Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) and Customer Engagement Platforms (CEPs) is crucial. While their objectives may overlap, their primary functions and applications vary significantly.
This article aims to define these differences, underscore the unique roles of CEPs and CDPs, and provide real-world use cases for both platforms.
What Is A Customer Data Platform (CDP)?
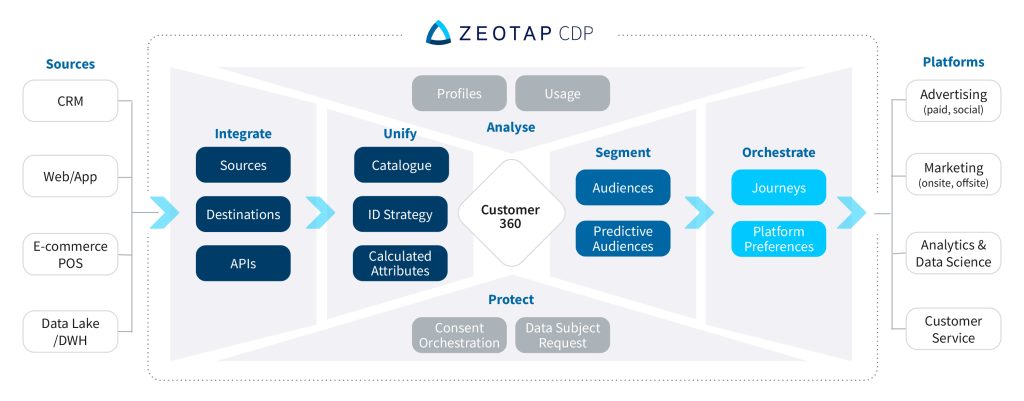
A CDP is a software that aggregates customer data collected from multiple channels and sources, structures it into a unified customer profile, and then allows other systems to access that data. It enables businesses to manage and analyse data in a compliant and structured way and efficiently deliver targeted, personalised customer experiences at scale across the whole customer journey.
To build the customer profiles, Customer Data Platforms combine a wide variety of data from multiple sources, with a focus on first-party data. In addition, CDPs may also be able to use second-party and third-party data. They collect it, for example, from your CRM, social media platforms, websites or mobile apps, event marketing, email marketing, and/or POS systems.
Having all the data about one customer stored in one platform allows companies to better understand what that customer really wants, analyse and predict customer behaviour, and tailor marketing and communication campaigns to the customer’s individual preferences. For example, knowing a customer’s privacy preferences can help decide how many targeted ads to send them.
What Is A Customer Engagement Platform (CEP)?
A Customer Engagement Platform is a software solution that allows organisations to interact with their customers across different channels and touchpoints with the aim of building stronger relationships, increasing customer satisfaction and driving business growth. For example, these platforms allow you to send targeted messages over multiple communication channels such as email, social media, messaging apps, and SMS to engage with customers in a personalised manner.
Additionally, CEPs facilitate the automation of routine tasks such as sending follow-up emails, responding to customer enquiries or triggering notifications based on customer behaviour.
Core Functions and Benefits of CDPs and CEPs
Broadly speaking, a CDP helps organisations to know who their customers are, while a CEP is designed to help them understand how best to engage with those identified customers. They both serve distinct yet complementary functions in the realm of customer data management and engagement.
Let’s delve deeper into the core functions and benefits of each:
Core Functions and Benefits of CDPs
CDPs serve as centralised repositories, housing a wealth of information ranging from demographic details to purchase histories and beyond. By consolidating data from first-party, second-party, and third-party sources, CDPs empower businesses with a holistic understanding of their customers.
Beyond creating a unified customer database, CDPs offer several key benefits:
- Personalised Experiences: Armed with comprehensive customer profiles, businesses can craft highly personalised experiences tailored to individual preferences and behaviours. Whether it’s delivering targeted marketing campaigns or providing personalised product recommendations, CDPs enable businesses to engage customers on a deeply personal level. For instance, Zeotap CDP provides out-of-the-box no-code models to identify and target audiences and allows for easy activation across multiple destinations and channels.
- Data Compliance and Privacy: With data privacy regulations becoming increasingly stringent, ensuring compliance is paramount. CDPs provide robust mechanisms for data consent management, governance, and security, safeguarding sensitive customer information and maintaining regulatory compliance. Zeotap CDP, for example, comes with a self-serve interface for privacy and compliance tasks that allows easy compliance with GDPR, CCPA, and other privacy frameworks.
- Analytics and Insights: CDPs offer powerful analytics and reporting capabilities, allowing businesses to derive actionable insights from their customer data. By analysing trends, identifying patterns, and understanding customer behaviour, marketing teams can optimise their strategies, and drive business growth. With Zeotap CDP, you can also create charts and visualisations to understand behaviours and trends.
Core Functions and Benefits of CEPs
In contrast, CEPs are designed to facilitate customer interactions and engagement across multiple touchpoints. These platforms enable businesses to deliver targeted messages and automate engagement processes, fostering stronger relationships and driving customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Key functions and benefits of CEPs include:
- Multichannel Engagement: CEPs empower businesses to engage with customers wherever they are, be it through email, social media, messaging apps, SMS, or other communication channels. This multichannel approach ensures that businesses can reach customers at every stage of the customer journey.
- Targeted Messaging: Leveraging data insights, CEPs enable businesses to deliver highly targeted messages and content to specific segments or individuals. By personalising communications based on preferences, behaviours, and demographics, businesses can increase the relevance of their messages and improve engagement rates.
- Automation: CEPs streamline engagement processes through automation, saving time and resources while improving efficiency. Tasks such as sending follow-up emails, responding to customer inquiries, and triggering notifications based on customer behaviour can all be automated, allowing businesses to focus on delivering exceptional customer experiences.
- Cross-Channel Consistency: With CEPs, businesses can ensure consistency in messaging and branding across all communication channels. This cohesive approach helps reinforce brand identity and provides customers with a seamless experience regardless of the channel used for engagement.
CDP vs CEP: What Are The Key Differences?
While both CDPs and CEPs play crucial roles in managing customer data and facilitating interactions, they differ significantly in their primary focus and functionality. Let’s explore the main differences between CDPs and CEPs:
1. Focus and Functionality
- CDPs: The primary function of a CDP is to aggregate and manage customer data from various sources, both online and offline, creating unified customer profiles. These unified customer profiles then serve as the basis for any kind of analysis, segmentation or targeting. They are also capable of breaking down the data silos across multiple platforms and sources. Overall, these platforms prioritise data aggregation, structuring, and analysis to provide businesses with comprehensive insights into their customers.
- CEPs: In contrast, CEPs are geared towards enhancing customer interactions and engagement across multiple channels. These platforms focus on delivering targeted messages, automating engagement processes, and fostering stronger relationships with customers.
2. Data Management
- CDPs: CDPs operate through a systematic algorithm. They excel in data aggregation and management, consolidating data from diverse sources. They ensure that customer data is organised, structured, and accessible for analysis, segmentation and activation across multiple platforms.
- CEPs: While CEPs also rely on customer data to deliver personalised experiences, their primary function is to facilitate engagement rather than data management. They leverage data insights to create tailored engagement strategies, deliver targeted messages and automate engagement processes across various channels.
3. Compliance and Privacy
- CDPs: Given their emphasis on data management, CDPs prioritise compliance and privacy standards in handling customer data. They provide mechanisms for data consent management, governance, and security to ensure compliance with regulations such as GDPR and CCPA.
- CEPs: CEPs focus more on engagement rather than data governance. However, they still adhere to compliance standards and often integrate with CDPs to ensure data management and compliance.
4. Use Cases
- CDPs: Common use cases for CDPs include customer segmentation, personalised marketing campaigns, predictive analytics, and improving customer experiences. They excel in handling real-time data.
- CEPs: CEPs are utilised for activities such as multi-channel messaging, campaign management, customer journey mapping, real-time customer engagement, automated responses, customer feedback management, and loyalty program management.
5. Integration
- CDPs: CDPs often integrate with various systems and platforms across the organisation, including CRM systems, marketing automation tools, analytics platforms, and more.
- CEPs: Similarly, CEPs integrate with communication channels and automation tools to streamline engagement processes and ensure consistent messaging. Integration with CDPs also allows CEPs to leverage comprehensive customer data for more effective engagement strategies.

By the way: When it comes to finding the right platform for your marketing needs, you should also be aware of the differences between CDPs and DMPs and between CDPs vs CRMs. We cover both in detail on our blog. It’s worth a read.
Should Brands Use CEPs or CDPs?
The choice between CDPs and CEPs completely depends on organisational objectives, priorities, and resource allocation. Brands should assess their specific needs, consider their long-term goals, and evaluate the capabilities of each platform to determine which solution best aligns with their business objectives and customer engagement strategies.
In general, CDPs are ideal for brands that prioritise comprehensive customer insights and personalised experiences. They are particularly beneficial for:
- data-driven marketing
- customer journey optimisation
- compliance and privacy management
For example, brands looking to leverage data insights for targeted marketing campaigns, personalised product recommendations, and tailored messaging can benefit greatly from CDPs. Overall, Customer Data Platforms are suitable for brands across various industries, including Retail and Ecommerce, Telco, Sports and Entertainment, Automotive, and Financial Services. They are designed for organisations seeking to centralise customer data, gain actionable insights, and deliver personalised experiences at scale.
CEPs are ideal for brands looking to enhance customer interactions, drive engagement, and foster stronger relationships across multiple channels. They are particularly beneficial for:
- multichannel engagement
- automation
- customer satisfaction and loyalty
For instance, tasks such as sending follow-up emails, responding to customer inquiries, and triggering notifications based on customer behaviour can all be automated, saving time and resources. Altogether, Customer Engagement Platforms are suitable for organisations across various industries, including Retail, Hospitality, Telco, and Healthcare, that seek to streamline engagement processes, deliver targeted messages, and drive customer loyalty through personalised interactions.
Best of Both Worlds: Integrate CDP and CEP
However, the question of whether companies should use a CDP or CEP does not necessarily have to be all or nothing. In some cases, integrating both CDPs and CEPs may provide the best of both worlds, enabling brands to leverage comprehensive customer data for targeted engagement and personalised experiences across every touchpoint.
Both CDPs and CEPs play pivotal roles in navigating the landscape of technology-driven marketing. They each address distinct challenges that businesses encounter. While CDPs consolidate data from various tools and sources to create a unified customer view, CEPs enable brands to meaningfully engage with their customers across multiple channels. Businesses require both to optimise their marketing efforts effectively.
Thanks to CDPs, CEP platforms are enriched with valuable customer data. Leveraging this data, CEPs segment customers intelligently and tailor interactions to suit their preferences, all while communicating insights back to the CDP. This seamless integration benefits not only the apps integrated with the CDP and the CEP but also the business and, most importantly, the customer.
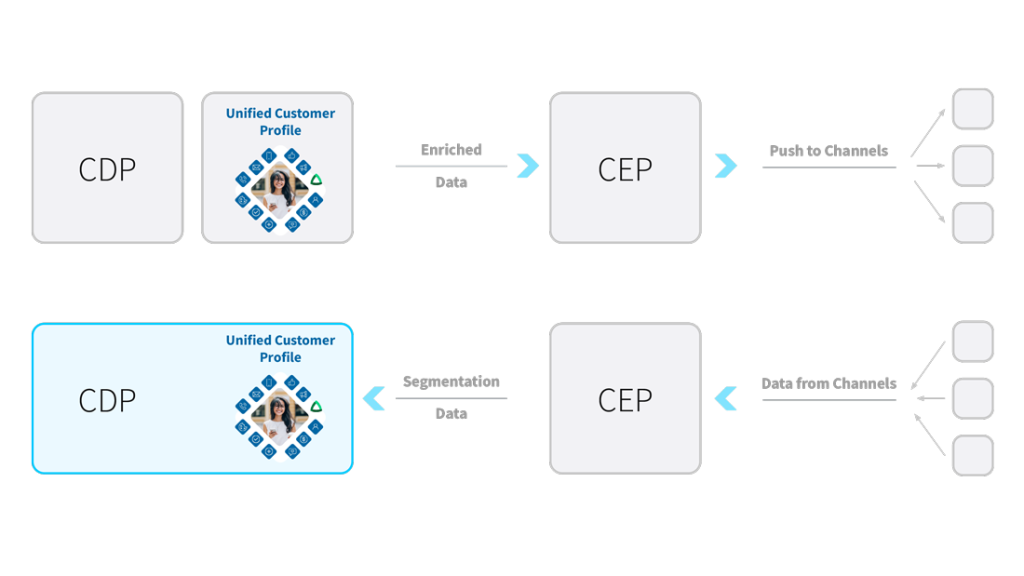
The more insights brands and retailers possess about their customers, the more effective their personalisation efforts become. Enhanced personalisation translates to greater customer satisfaction, leading to improved retention, conversion rates, and ultimately, better business outcomes.
All in all, both CDPs and CEPs are integral components closely aligned with this personalisation strategy. Businesses that leverage this dual-stack approach gain a competitive edge in the market. This is why, for example, Zeotap CDP also offers integration with leading CEPs such as Batch and Airship, so that companies can maximise the value of their customer data and optimise their interaction strategies.
The Bottom Line of CDP vs. CEP
In summary, while CDPs focus on aggregating and managing customer data to provide unified views and provide personalised experiences, CEPs specialise in facilitating interactions and engagement across multiple channels to foster stronger relationships and drive customer satisfaction.
Understanding these key differences is essential for businesses seeking to optimise their customer engagement strategies and deliver exceptional experiences across every touchpoint. Ultimately, in practice it is usually a combination of CDP and CEP that really drives companies forward and enables effective marketing: CDPs provide the data insights, enabling CEPs to provide personalised, targeted customer communications.





