Segmentation is nothing new to marketers. However, marketing segmentation traditionally involved simple things like demographics and geographical location. Now – with behavioural segmentation – marketers can divide customers into groups based on the way they behave too.
This guide explains behavioural segmentation with examples, its role in marketing, the main types of behavioural segmentation, and the best strategies and tools to use.
What is Behavioural Segmentation?
Behavioural segmentation is an audience segmentation approach used in marketing to divide customers into groups based on customers’ behavioural data points and purchasing habits — e.g., by what actions they take, not their age or gender. Each group has specific behavioural patterns, which make it easier to send targeted marketing materials to them.
Behavioural segmentation falls under the broader marketing segmentation but distinguishes segments specifically based on customers’ behavioural data points.
Behavioural Segmentation in Marketing
Behavioural segmentation in marketing involves dividing customers into groups based on their actual behaviours. Customer segmentation is based on similarities in their behavioural patterns – what they do, not who they are, such as:
- Purchase history;
- Channels used — mobile or desktop, social media or email;
- Frequency of purchase;
- Types of products bought;
- Types of content consumed;
- Response to past marketing campaigns.
By analysing behavioural customer data, companies can identify distinct customer segments tied to shared engagement patterns. It allows businesses to create highly targeted marketing strategies for each behaviorally defined segment. In turn, it helps to reduce and optimise the media budget spent on customer acquisition.
Data sources typically include transaction records, website usage tracking, loyalty program activities, online and offline data, and data enrichment techniques, all of which can be easily tracked in a customer data platform (CDP) such as Zeotap CDP.
Discover how advanced segmentation with Zeotap CDP’s Audiences module can transform your customer insights and campaigns.
Behavioural Segmentation Examples
Behavioural segmentation characterises audience segments specifically based on their behavioural habits. The most common actions or behaviours to track in behavioural segmentation are:
- How did your audience become a customer (customer acquisition);
- How they have gotten there (customer journey);
- How often do they purchase or interact (engagement);
- How long will they buy or use the product (customer retention).
For example, customers who primarily make purchases online within a week of showing engagement on your company’s social media channels represent a distinct behaviour.
Here’s another behavioural segmentation example: One group of customers buy cod liver oil tablets because they’re good for eye health. Another group buys them because they’re the cheapest on the market. These customers can be divided and marketed separately, focusing on what matters to each of them.
Below we will take an in-depth look at the main types of behavioural segments, how they work, and why behavioural segmentation is important. Plus, you’ll learn about the benefits of using behavioural segmentation in your marketing campaigns.
Why is Behavioural Segmentation Important?
Behavioural segmentation is important because it provides actionable customer insights for marketers. By understanding customers based on their actions rather than characteristics alone, companies can develop more:
- Personalised marketing strategies — right messaging to most relevant customers;
- Optimised budget allocation — through increased purchases, conversions, and customer retention rates;
- Future forecasting — identify past trends to plan for future campaigns.
This helps to improve business outcomes. For example, by reducing the marketing budget spent on irrelevant customer groups that are less likely to make a purchase and spending more budget on high-converting customers as the campaigns have been targeted toward their behaviours.
What Are the Four Types of Behavioural Segmentation?
In most cases, you’ll be able to divide the majority of your customers in four behavioural groups. In this section, we’ll explore these four main types of behavioural segmentation — each offering a distinct lens through which to view and engage with your audience.
1. Purchase Behaviour
Usage and purchase behaviour relates to how customers use a product and how they behave during the decision-making process. This is one of the most important types of behavioural segmentation because it allows businesses to improve the purchasing process.
There are four main categories of purchasing behaviour:
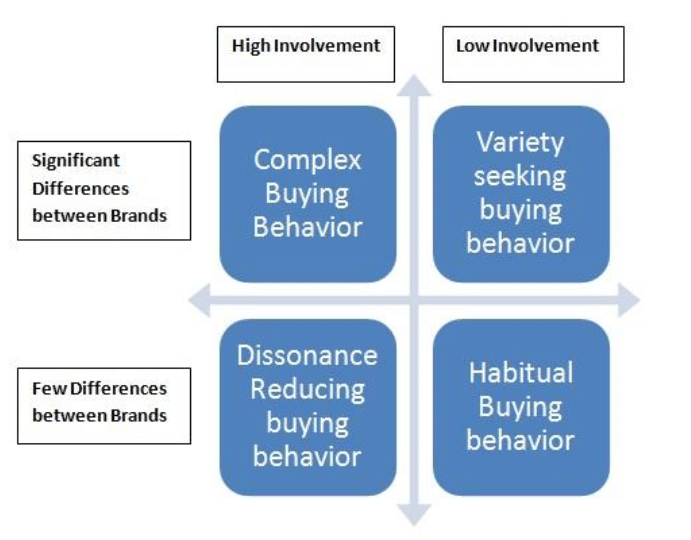
Source: clootrack.com
- Complex: This is when a purchasing decision is complex and the customer considers a lot of different factors. For example, if a customer is buying a new laptop, there are several things they’ll think about, such as RAM, screen resolution, brand, storage, etc.
- Habitual: Every consumer makes habitual purchases. They’re normally small purchases you buy regularly. For example, some customers buy Jif Peanut Butter and would never buy Skippy Peanut Butter. There isn’t much difference between the two – they do so out of habit.
- Dissonance reducing: When a customer is making a large purchasing decision, they might look for one factor that separates two products. For example, if two cars have similar specs, they might go for the cheaper option.
- Variety seeking: Sometimes, customers will try a new product to see how it stacks up. For example, if they normally drink Nescafe instant coffee, they might try Starbucks for a change.
Understanding which category of purchasing behaviour a customer falls into can help you deliver targeted messages. For example, if a customer belongs in the complex category, you need to drive home the benefits of your product over its competitors. If they fall into the habitual category, you just need to send a gentle reminder. Identifying this should form part of your processes mapping.
2. Occasion and Time-Based
Time-based segmentation is about the timing of when a customer purchases. You can divide customers into three different groups based on when they buy:
- Promotional buyers: These are customers who make purchase decisions according to special offers and discounts. They’re a great opportunity for businesses to increase sales with limited investment by driving traffic during key times.
- Seasonal: These are customers who buy products based on the season. During the summer, they’re more likely to purchase beachwear. In the winter, they might look for sweaters and coats. For example, in America, you’ll see Christmas-related goods appearing in stores as early as October/November.
- Occasion-based: These are customers who choose to make a purchase based on an event or occasion. For example, Valentine’s Day or Mother’s Day.
Understanding this type of behavioural segmentation allows you to optimise sales at different times of the year. Features like audience segment refresh by Zeotap CDP can help marketers ensure campaigns are activated in a timely manner to capture the target audience’s attention.
3. Benefit Driven
Benefits are important to all customers. However, the reasons they’re important can differ greatly. Two companies might want a piece of content management software for two completely different reasons. One could wish to create a content marketing strategy for SaaS while the other wanted to build a website. Understanding what benefits your customer is interested in will help you market your products to them.
4. Customer Loyalty
Customer loyalty and understanding them is the real secret to business. It’s important to recognise why your customers stay true to you. This information can be gained from customer questionnaires. Then you can optimise these customers via loyalty schemes and other marketing campaigns.
Loyal customers are like gold dust for a business. Here’s why:
- They continually buy your product or service;
- It’s cheaper to retain them than to acquire new customers;
- They have the highest lifetime value of all customers.
Other Types of Behavioural Segmentation
In addition to the four main types of behavioural segmentation, there are a few other ways to group customers.
1. Customer Lifecycle Stages
The five customer lifecycle stages are reach, acquisition, conversion, retention, and loyalty. Knowing where a customer falls on this path can help you deliver targeted messages. For example, if they’ve already bought a product from you, thank them for their purchase and encourage them to buy again with a personalised offer.
2. Customer Engagement Level
This relates to how much a customer engages with your brand. Your brand is more than just visual aspects. Even if you use the best logo maker and create an appealing brand image, there’s still some work to do to engage customers. This is most useful for service-based businesses. There are three levels of user engagement:
- Occasional: A customer’s engagement with your brand is sporadic. They only connect with you when they need to and ignore marketing messages.
- Regular: A customer engages with your brand regularly but doesn’t use every product or service.
- Intensive: A customer uses your service daily and it’s important to their life and/or work. This is a good reason to provide them with special treatment.
3. Value-centric Customer Segmentation
Value-centric customer segmentation involves dividing customers based on their potential value to the business. It categorises customers according to their economic benefit through profitability, revenue, and lifetime value. Businesses analyse purchase data and behaviour to assess customer worth.
Therefore, high-value groups generating more revenue receive tailored offers to enhance loyalty. Lower-value segments see efforts to boost engagement until they contribute more. This targeted value-centric approach allocates resources strategically based on value, improving satisfaction, retention and business outcomes.
4. Customer Satisfaction
This segment relates to customer feedback. You adjust your message based on how the customer feels about your product or service. For example, if a customer is dissatisfied, you don’t want to send them a message telling them how great your product is.
Behavioural Segmentation Benefits
One of the key behavioural segmentation benefits is hyper-personalisation. But what are some other key advantages of behavioural segmentation, and why is hyper-personalisation in marketing beneficial?
With behavioural segmentation, businesses can tailor marketing strategies to meet the nuanced preferences and behaviours of different customer groups. Some of these behavioural segmentation benefits include:
- Enhanced personalisation;
- Improved customer experience;
- Increased efficiency in marketing spend;
- Higher conversion rates;
- Better customer retention;
- Deeper insights into customer preferences;
- Ability to predict future behaviours;
- Increased customer lifetime value (CLV);
- Improved customer service.
Let’s dive deeper – here’s a detailed look at the key behavioural segmentation advantages:
1. Personalisation
Behavioural segmentation allows businesses to craft personalised marketing messages based on the specific actions and behaviours of customers. By understanding how different groups engage with products or services, companies can create targeted campaigns and communication that resonate more deeply with each segment, leading to increased engagement and customer satisfaction.
2. Improved Customer Experience
When you know your customers’ behaviours, you can design experiences that are more aligned with their expectations and needs. For example, if data shows that a segment of customers frequently purchases products for specific occasions, businesses can optimise their marketing efforts to these times, enhancing the overall customer experience and increasing relevance.
3. Optimised Marketing Spend
By targeting only those segments that are most likely to respond to specific offers or messages, businesses can allocate their marketing budgets more effectively. This targeted approach reduces waste on broad campaigns that do not resonate with a large portion of the audience, thereby optimising marketing spend.
4. Higher Conversion Rates
Marketing campaigns that are based on behavioural segmentation are generally more effective in converting prospects into customers. When customers receive offers and messages that are aligned with their previous behaviours, they are more likely to find the content relevant and take the desired action, whether it’s making a purchase, signing up for a newsletter, or participating in a loyalty program.
5. Better Customer Retention
By continually meeting the needs and expectations of each customer segment, businesses can improve customer loyalty and retention. Loyal customers are more profitable in the long run, as they tend to purchase more over time and are cheaper to retain than acquiring new customers.
6. Deeper Insights into Customer Preferences
Behavioural segmentation also provides valuable insights into evolving customer preferences and market trends. Businesses can use this data to innovate or improve products and services, ensuring they stay competitive and relevant in their market.
7. Predict Future Behaviours
With a robust understanding of past customer behaviours, companies can better predict future actions. This predictive capability enables proactive campaign planning and product development, anticipating customer needs before they even arise.
8. Increased Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
Customers who receive highly personalised and relevant content are more likely to continue engaging with a brand over time. This ongoing engagement increases the lifetime value of customers, as they continue to make purchases and interact with the brand.
Behavioural segmentation transforms generic marketing efforts into highly focused and effective strategies that significantly boost customer engagement, satisfaction, and profitability.
9. Improved Customer Service
The key to excellent service is understanding the customer. With behavioural segmentation, it’s possible to adjust service messages based on the type of customer. To do this effectively, adopt intelligent automation in your customer service process.
Behavioural Segmentation Strategies
Now, let’s look at some behavioural segmentation strategies and how you can actually use them. Whereas segmentation types define the behavioural metrics for categorising customers, strategies describe how those behaviorally defined segments can then be engaged through various marketing methods.
Here are some examples of behavioural segmentation strategies:
1. Retarget
Retargeting programs re-engage website visitors or app users who previously showed interest in a brand or product but did not complete a purchase.
For example, an online clothing store identifies visitors who viewed a particular dress but didn’t buy it. Through behavioural segmentation, the store recognizes these customers as “considering” the dress and retargets them on social media with a 15% off promotion specifically mentioning the dress to incentivize purchase.
2. Offer similar products
Cross-sell and upsell promotions target related or higher-priced products to existing customers based on their purchase history.
For example, an online DIY retailer identifies customers who regularly purchase paint but have never purchased paintbrushes. These customers are recognized as needing new paintbrushes. The retailer targets this segment with an email promoting paintbrushes, thereby cross-selling a complementary product.
3. Loyalty messaging
Retailers often implement loyalty programs to reward and encourage repeat purchases from their most valuable customers who can be engaged in tailored ways.
For example, a grocery store analyses shopping patterns and identifies a customer segment that consistently spends $300+ monthly on a specific brand. These loyal shoppers receive a personalised email highlighting exclusive discounts for them.
4. Predict future behaviour
You can’t predict the future, but you can try to forecast it using predictive modelling. Machine learning on customer behavioural data can help predict customers’ future actions.
For example, an online retailer analyses past purchase patterns and identifies customers whose spending peaked three months ago and has since declined. This cluster can be targeted with personalised offers or coupons to re-engage their interest, with the goal of preventing customer churn.
Customer Segmentation Tools
There are various tools marketers can use to segment customers based on their behaviour. Here are some of the best types of tools to use for customer segmentation:
- Customer data platforms (CDPs) — Collect, harmonise and activate customer insights across systems to populate attributes for segmentation. Examples include Zeotap CDP or Segment.
- Customer relationship management (CRM) systems — Centralised customer database with functionality to analyse profiles and behaviours and segment customers. Examples include Salesforce or Hubspot.
- Data management platforms (DMPs) — Consolidate first and third-party customer data from varied sources to create a unified profile. Examples include Adobe Audience Manager or Oracle BlueKai.
- Survey tools — Segmentation based on attitudinal data via surveys. Examples include Qualtrics or SurveyMonkey.
- BI and visualisation tools — Create dashboards for customer segments, metrics and trends. Tools include Looker, Tableau, or Power BI.
How to do Behavioural Segmentation?
With the Zeotap CDP audience segmentation module, you can automatically divide audiences based on behavioural traits like recency, frequency, and monetary value without requiring coding skills, and leverage pre-built segments for speed and ease of use.
What’s more, you can directly activate the segments across channels with just one click, whether email, display ads, or mobile push notifications. Marketers can also get insights into how big each audience segment is and if there are any overlaps behind the behavioural patterns.
Moreover, using predictive analytics, marketers can also identify at-risk users to proactively create retention campaigns. Zeotap CDP brings online and offline data 360-degree view, giving a holistic overview which makes it easier to build behavioural profiles.
When Using Behavioural Segmentation, Keep This in Mind
Behavioural segmentation could be the key that unlocks your business’s success. However, it’s not the only tool you’ll need to employ. Behavioural audience segmentation provides a framework for communicating directly with your customers, but you still need to decide what to say.